In this article, we will briefly discuss the computer and its components: Definition, Components, and processing of a computer.
Definition:
A computer is an electronic machine that takes data as input, processes it, and displays it as output. Data is an organized form of raw materials, facts, and figures. The computer processes the data and then it is converted into useful information and sent as output. It is also capable of storing data for later use. The computer consists of the following core components:
- Input Devices
- System Box
- Storage Devices
- Output Devices
First, we are discussing the processing of computers also known as the information processing cycle.
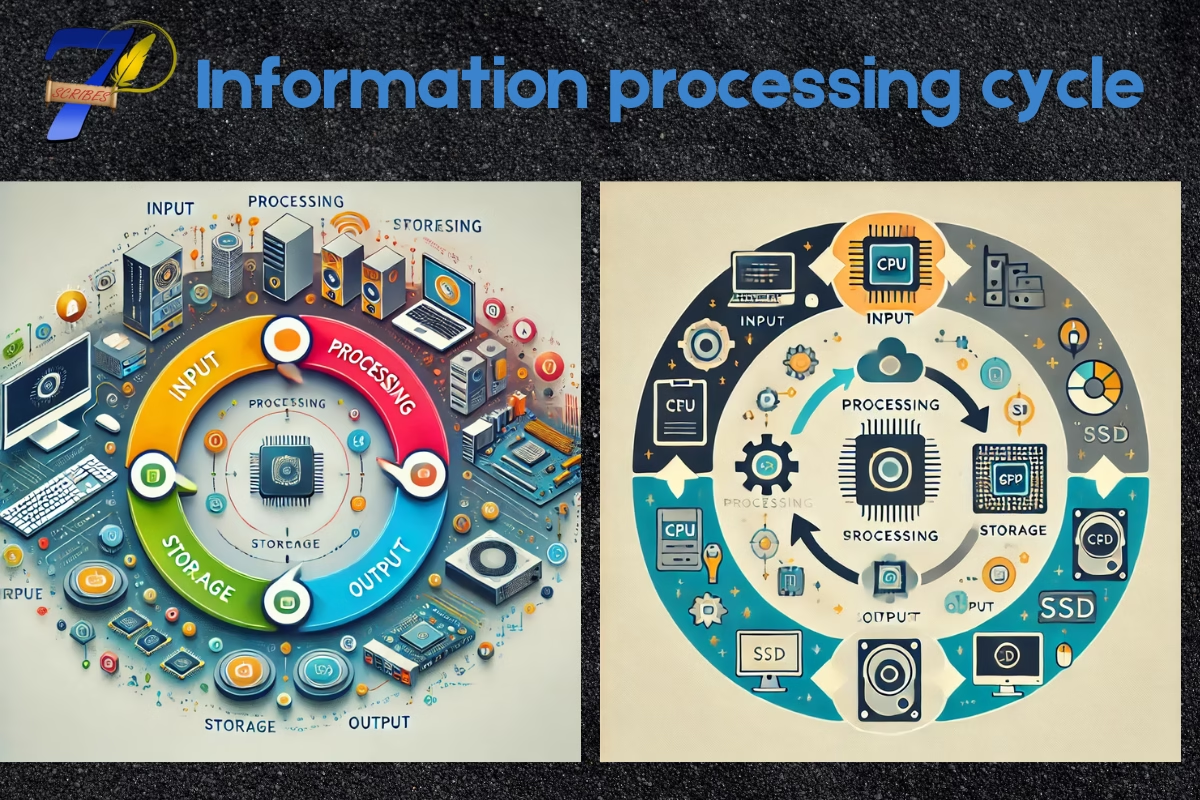
Information Processing Cycle
There are following four information processing cycles:
-
Input:
The first step of the cycle is to take data as input from the user. Data are unorganized from facts, figures, or raw materials. It can also be referred to as unorganized information. After taking input from the user, the data is sent to the processor for processing.
-
Processing
In this step, the process applies some processes to the data and converts it into useful information. Then, it’s sent to the storage devices or output.
-
Storage
Storage devices are devices that have the functionality or capability to store data or information. The process data is stored in storage devices for further use or future use.
-
Output
It is the last step of the cycle in which information is displayed to the user. Either in soft form or hard form.
Computer and its Components:
-
Input Devices:
The devices that are used for input are called input devices. These devices are connected to the computer with ports in the system box. The primary input devices are the keyboard and mouse:

A keyboard consists of keys that are used to input different things or data to a computer. It consists of numeric keys, special keys, alphabet keys, function keys, and alphanumeric keys. Generally, there are about 109 keys on the keyboard.
There are different types of keyboards, like gaming keyboards, QWERTY, Standard, Ergonomic compact keyboards, etc.
-
Mouse
The mouse is also a primary device that helps the user to navigate on the screen. The mouse has two buttons left and right and a scroll wheel at its center. The mouse interacts with the graphical icon on the screen to perform activities. There are many types of mice, Wired mouse, wireless, mechanical, optical or laser mouse, etc.
-
System Box
The system box is a medium size compact box that consists of a motherboard. The Mother Board is a circuit that controls all the activities of a computer. The central processing unit or simply processor is also present on the motherboard. It has many ports through which many other output devices are connected to the computer like HDMI, USB Ethernet Port, etc. It controls all the power supply to the computer. It has a fan that cools down the computer.

Two basic units in the central processing unit take part in processing are
-
Arithmetic and Logic Unit
The arithmetic unit of the computer is responsible for performing basic mathematical calculations like Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication and Division on data.
The logic unit is responsible for or takes part in making decisions like AND, OR, and NOT, etc.
-
Control Unit
The control unit monitors all the activities of the computer and also manages it.
Types of System Box:
- Tower cases
- Desktop cases
- Small Form Cases
- All in one Cases
- Rack Mount Cases
- Customize Cases
-
Storage Devices
The devices that are used to store data. These devices allow computers to store data for future use. Data is stored in storage devices by using various technologies like laser, magnetic, etc. There are two main categories of Storage devices:

Primary storage devices and secondary storage devices.
-
Primary Storage Devices
Primary storage devices play an important role in computer processing. It is also known as volatile memory means it becomes free after the power is disconnected. For example:
RAM (Random Access Memory), Cache Memory, etc.
-
Secondary Storage Devices
Secondary storage devices are used to store data permanently. It is also called nonvolatile memory. For example, Hard Disk Drive (HDD), Solid State Drive (SSD), etc.
-
Output Devices
The devices that are used to display output to the user are called output devices. The output generated by output devices is either called softcopy or hardcopy. The primary output device is:

Monitor:
The monitor is a display screen that displays the output on the screen. Users always interact with the computer with the monitor. It is also an output device. The older monitor has a 16:9 width-height ratio screen. But, nowadays different width and height ratio screens available in the market. It can be made up of LCD (liquid crystal technology), LED (light emitting diodes), CRT (Cathode Ray tube), OLED (organic LED), etc.
FAQ’s:
- What is meant by the Information processing Cycle?
ANS: Information Processing Cycle:
The information processing cycle is the duration through which a computer converts data into useful information.
- What is meant by Volatile memory?
ANS: Volatile Memory:
The type of memory which loses its data whenever power is disconnected and cannot be recovered. This type of memory is usually used for processing.
- What is Meant by Non-volatile memory?
ANS: Non-Volatile Memory:
The type of memory which not lose its data whenever power is disconnected and can be recovered. This type of memory is usually used for long-term storage of data.
- What is meant by Softcopy output?
ANS: Softcopy Output:
The output generated by output devices on the display screens is called softcopy output.It is not tangible but changeable.
- What is hardcopy output?
ANS: Hardcopy Output:
The output generated by output devices on the paper is called softcopy output. It is tangible but not changeable.
- What is a port?
Ans: Ports:
Ports are the interface through which external devices are connected to the computer. The computer has many types of ports like USB ports, HDMI ports, Ethernet ports, etc.