In today’s data-driven world, edge computing is changing data processing. According to Gartner, 75% of data will be processed at the edge by 2025. But what exactly is edge computing, and why is it becoming so critical?
Traditional cloud computing is powerful, but it has issues when handling huge amounts of data produced by modern technologies like smart devices (IoT), self-driving cars, and smart cities. Issues like bandwidth limitations, latency, and congestion make processing data in real time difficult. This is where edge computing comes in. Edge computing processes data that is closer to the source. It makes things faster, secure, and efficient.
What is edge computing?
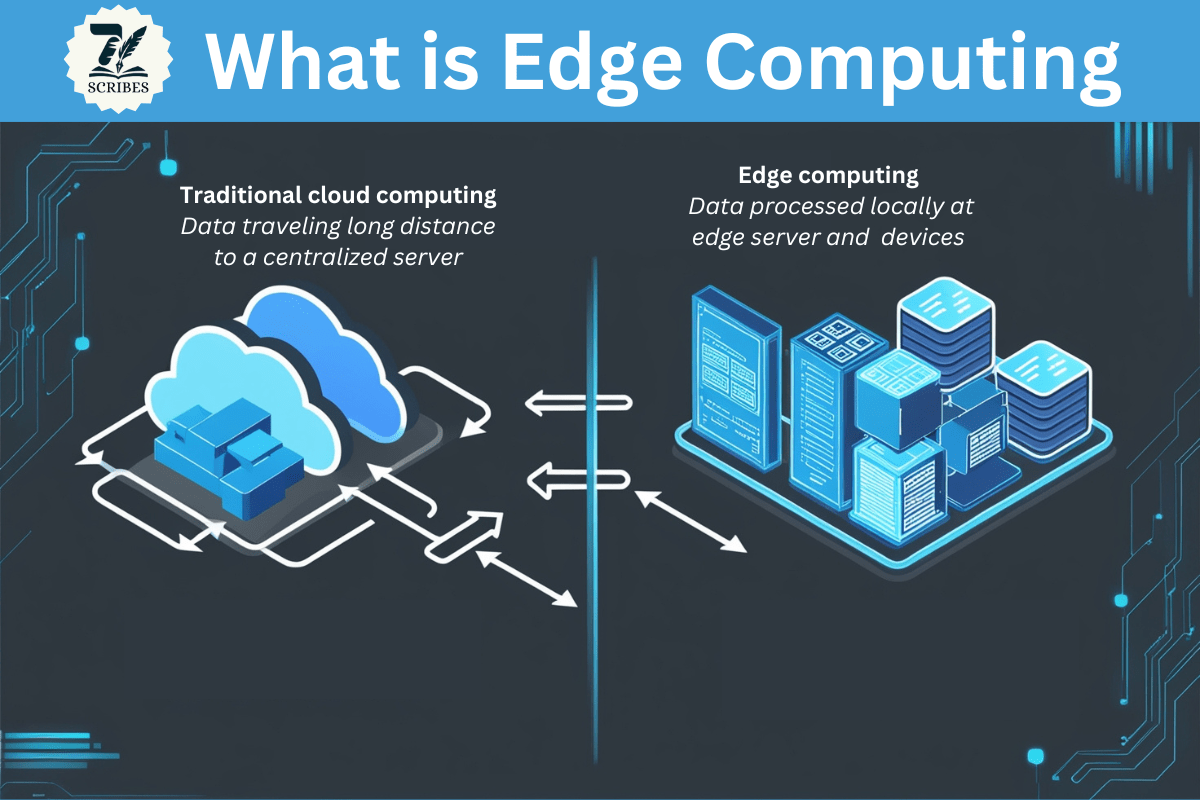
Edge computing is a distributed computing technology where data is processed at the network’s edge. In simple terms, it is where data is processed at the source or a server that is close to the source. Instead of sending all data to the centralized server, edge computing processes data locally, either at the source device or edge server, which is close to that source. This reduces the distance that data must travel in case of cloud computing. It improves efficiency and accuracy.
How does edge computing work?
Edge computing solves the three main challenges to make real-time functionality for smart devices and IoT sensors. And the challenges are
Connecting devices to a network from a remote location:
Isolated locations such as oil rigs and farms require a solid connection to deliver enormous amounts of data to the cloud, something that is highly challenging.
Edge computing enables devices to process data in the exact locations where they’re created without relaying all of it to the cloud. As a result, they can perform well even when there’s no good Internet.
Slow data processing:
Sending everything to the cloud takes time, which can cause delays (latency) in getting the result. It is a critical issue where an immediate response is required. Such as self-driving cars or factory machines.
Edge computing processes data locally from where data is generated. It makes things faster because the data does not need to travel a long distance.
For Example, A smart camera can detect a problem instantly instead of waiting to send footage to the cloud.
Edge devices cause bandwidth problems:
In cloud computing, when too many devices send data to the cloud simultaneously, it can overwhelm the network, making everything slower.
Edge computing reduces the amount of data sent over the network by processing most of it locally. Only important information (like alerts or summaries) is sent to the cloud. This keeps the network running smoothly and saves bandwidth.
In traditional cloud computing, data produced by the user’s computer traveled across a Wide Area Network (WAN) such as the internet, through the corporate Local Area Network (LAN), from where data is stored and performed operation on it. The result then returned to the user’s computer. It is still an effective approach in client-server computing.
Edge computing addresses all these problems by processing at the source or the edge server that is near to the source. In edge computing, all the data produced by the computer is not sent to the centralized server. Only important information or data is sent to the server. Other data or information is processed at the source. It reduces the time required to transfer all the data to the server. It also increases security because most of the data is processed locally.
Why is Edge Computing Important?
Edge computing is important because it makes things faster, safer, and more efficient.
Enhanced Productivity:
Edge computing supports enterprises to optimize operations by processing the huge amount of data rapidly at the source (ideal case) or near the source where the data is produced. This is very efficient instead of sending everything to the centralized cloud, which would cause network delays.
Reduced Latency:
Edge computing helps companies to process data much faster and reliably because it does not need to send all data to a central server or cloud. Instead, data is processed where it is generated.
Imagine thousands of IoT (Internet of Things) devices like cameras, sensors, and smart homes trying to send data simultaneously. This can cause delays (Latency), congestion, and even reduced data quality.
With edge computing, devices near the edge of the network can process data instantly.
Reduced Costs:
With edge computing, businesses can reduce IT costs by processing data locally rather than in the cloud. Besides reducing companies’ cloud processing and storage costs, edge computing decreases transmission costs and time by processing the unnecessary data at or near the device where it is collected.
Enhanced Security:
For businesses, adding thousands of internet-connected devices (like cameras and sensors) to their network can increase risks. Edge computing reduces this risk by sending the necessary information to the cloud or data center.
Keeping offline storage and sending a limited amount of information to the cloud makes it difficult for hackers to access sensitive information. It means that businesses are less vulnerable to cyberattacks and keep their data safer.
For Example, if a machine is about to fail, edge devices can alert the right people or equipment immediately. This allows for quick action, preventing bigger problems and keeping everything running smoothly.
Better Work Efficiency:
Edge computing helps employees work faster and more efficiently.
Because it gives data at the time when they need it. Instead of waiting for information to come from a faraway cloud server. Edge computing processes data locally so that workers can access it immediately.
In smart workplaces, edge computing also keeps equipment and machinery in proper shape. For instance, it can forecast when a machine will malfunction and repair it before it can cause an issue. It is equal to less error and downtime, thereby allowing the workers to go on with their work uninterrupted.
Data Sovereignty:
It is a term that implies companies have to adhere to the data privacy laws of the country in which the data is being collected or retained. An example is the European Union’s extremely strict laws called GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) that protect people’s data.
When companies move data to the cloud or a data center in another country. It may be challenging to meet these regulations. But edge computing enables data to be processed and stored close to where it is collected. This makes it simpler for organizations to meet local regulations and keep data safe and confidential.
What is Edge Computing Hardware?
Edge computing hardware includes all the physical devices and equipment that help to process data close to where it is created. Instead of sending all the data to a faraway cloud server, these devices handle the work locally.
Key Components of Edge Computing Hardware:
Edge Devices:
These are the sensors or smart devices that collect data.
Examples:
- Smart cameras(like security cameras that detect motion).
- Thermometers(that measure temperature in real-time).
- Robots(used in factories to assemble products).
- Drones(used for surveying land or delivering packages).
- Vibration sensors(used to monitor machines for problems).
- Some of these devices have built-in memory and storage to store and process data on their own, while others rely on nearby servers.
Processors:
It is also called the brain of edge computing. It includes:
- CPUs(Central Processing Units): They handle general tasks.
- GPU(Graphics Processing unit): It is used for specialized purposes like video processing or AI.
- The more powerful the processor, the faster the system can work and handle multiple tasks at once.
Edge Servers
These are groups of powerful computers placed close to the source. They handle big tasks like running apps, analyzing data, or managing other devices.
Gateways:
These are placed between edge devices and the cloud. They:
- Enable wireless connections (like Wi-Fi or 5G).
- Provide security (like firewalls to block hackers).
- Process and send data to the cloud when needed.
Routers:
These devices connect different networks. For example:
A router in a factory might connect the local network (LAN) to the internet or a company’s wider network (WAN).
Switches (Access Nodes):
They are used to connect multiple devices (like cameras, sensors, and computers) so that they can share data and work together.
Comparison of Edge, Cloud, and Fog Computing
Cloud Computing: Cloud computing is a centralized architecture that depends on remote servers and data centers to process and store data.
Edge Computing: Unlike with cloud computing, edge computing is a decentralized computing technique in which data is processed at the edge rather than on a centralized server. It increases processing speed.
Fog Computing: Fog computing is also a distributed computing architecture designed to enhance edge computing. It increases the capabilities of edge computing by providing a layer of computing infrastructure between the edge devices and the cloud.
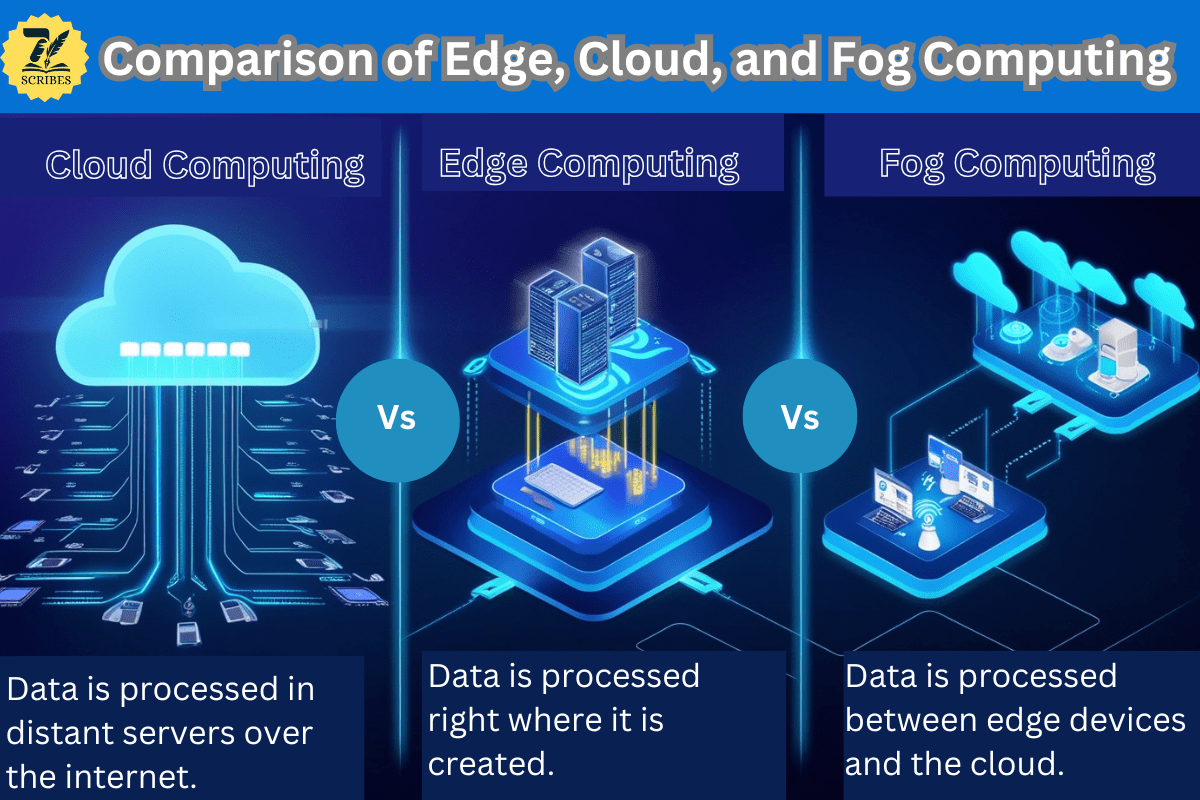
Key Differences
|
Aspect |
Cloud Computing |
Edge Computing |
Fog Computing |
|
Location |
Far away (remote servers) |
Right where data is created |
Between edge and cloud |
|
Speed |
Slower (data travels far) |
Fast (data stays local) |
Faster than cloud, slower than edge |
|
Use Case |
Long-term storage, big data |
Real-time processing |
Helping edge devices, filtering data |
|
Example |
Netflix streaming movies |
Smart camera detecting motion |
Smart building managing sensors |
Use Cases of Edge Computing
There are many application or use cases of edge computing. Some important application are
Edge Computing for Health Care
In health care edge computing are using in different ways which are
Vaccine Temperature Sensors:
It is used to prevent vaccine wastage. Vaccines need to stay at the right temperature to work. Sensors attached to vaccine shipments monitor the temperature in real time. If the temperature is too hot or cool, sensors can immediately alert the responsible person.
At Home Medical Devices:
Devices like smart CPAP (Continuous Positive Airway Pressure) or heart monitors can collect your health data at home. It can analyze data and send important information to your doctor instead of sending all data to a remote server. This helps your doctor to keep an eye on your health immediately.
Hospital Equipment Tracking:
Hospitals have many equipment, such as wheelchairs and gurneys. With edge computing, IoT devices can track devices in real time. This will help nurses find the devices without wasting time searching for them.
Patient Mentoring:
Many wearable devices can track a patient’s heart rate, oxygen levels, or other vital signs. Edge computing allows this data to be processed in the hospital so Doctors can get an immediate alert if something is wrong.
Autonomous Vehicles
Edge computing also used in autonomous vehicles. They need to react instantly to traffic, obstacles, and pedestrians. Edge computing processes data locally in the vehicle, making it easy to make real-time decisions. This ensures safer, faster, and more reliable autonomous driving.
Challenges of Edge Computing:
We know that edge computing has many benefits, but it also has a few challenges, which are
Addressing Bandwidth Challenges at the Edge
Edge computing reduces the bandwidth load between edge locations and centralized data centers by processing data centers. It shifts the burden on the LAN (Local Area Network) at the edge. As numerous devices are producing and processing the data locally, bandwidth demand within the edge locations increases. It can strain the underlying network architecture, resulting in bottlenecks, latency, and even loss of data.
The issue needs to be addressed by organizations allocating sufficient bandwidth to edge sites and upgrading their LAN infrastructure.
Security risk:
Edge computing processes data locally, which overcomes security risks but also brings new challenges. When computing occurs outside the core network, it is harder to create a strong security system to protect everything. To solve this problem, you can use cloud-based security tools. These tools help to apply security tools like who can access what (role-based access control).
Management Complexity:
When all data processing happens in one place, it is easy for administrators to monitor, manage, and analyze them. When computing resources disperse around the edge, management becomes more difficult. It increases the risk of mistakes. You need a centralized monitoring and orchestration solution to solve this issue. This tool acts as a single control point. It allows administrators to manage all edge systems from one place.
FAQ’s
Q1) What is edge computing?
Q2) Difference between cloud computing and edge computing?
Q3) What are the benefits of edge computing?




Amazing platform to learn Programming relate information and UpTo date the latest world problem…